In this tutorial, Argo CD is used for deploying a Argo Rollout and Keptn is used for testing, evaluating, and promoting this rollout. More precisely, in this tutorial, Argo CD is used as deployment tool and not the Keptn built-in tool called helm-service. Furthermore, this tutorial uses Argo Rollouts, which introduces a new custom resource called Rollout implementing deployment strategies such as Blue/Green and Canary.
This tutorial provides a sample Helm chart, which contains the carts and carts-db service. These services will be deployed into a production environment using Argo CD. Afterwards, Keptn will be used to test the carts service using performance tests. Using the resulting metrics provided by Prometheus, Keptn will then check whether this service passes the defined quality gate. Depending on whether the quality gate is passed or not, this service will be promoted or aborted. In case it will be promoted, this service will be released to real-users.
What you'll learn
- Use Argo CD and Argo Rollout for deployment
- Use Keptn for initiating the tests
- Use Keptn for automated deployment validation (aka quality gates)
- Use Keptn for promotion of microservices if they pass the quality gate
- A completed Keptn installation (i.e.
keptn installwith flag--use-case=continuous-delivery) - Basic knowledge of Argo CD and Argo Rollouts
- Completed Argo CD installation and the
argocdCLI needs to be logged in - Completed Argo Rollouts installation
- Clone example files used in this tutorial:
git clone --branch 0.7.3 https://github.com/keptn/examples.git --single-branchcd examples/onboarding-carts
The Keptn argo-service takes care of promoting or aborting a Rollout depending on the result of the quality gate. More precisely, the argo-service listens for sh.keptn.events.evaluation-done events and depending on the evaluation result (i.e. whether the quality gate is passed or not) the service promotes or aborts a rollout, respectively.
- The
argo-serviceis not contained in the default installation of Keptn.
To install theargo-service, execute:kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keptn-contrib/argo-service/0.1.1/deploy/service.yaml - The
gatekeeper-service(which is installed by the default installation of Keptn) has to be removed:kubectl delete deployment gatekeeper-service -n keptn
This tutorial sets up a single stage environment containing a production environment. In this stage, performance tests are used to test new deployments. For creating the project, the following shipyard is used:
stages:
- name: "production"
deployment_strategy: "blue_green_service"
test_strategy: "performance"
Create a new project for your services using the keptn create project command. In this tutorial, the project is called sockshop. The Git user (--git-user), an access token (--git-token), and the remote URL (--git-remote-url) are required for configuring an upstream. For details, please visit Git-based upstream where instructions for GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket are provided.
Before executing the following command, make sure you are in the examples/onboarding-carts folder:
keptn create project sockshop --shipyard=./shipyard-argo.yaml --git-user=GIT_USER --git-token=GIT_TOKEN --git-remote-url=GIT_REMOTE_URL
- Keptn manages all service-related artifacts (like testing files, SLOs, etc.),
in a so-called service.
Create a service for carts using thekeptn create servicecommand:keptn create service carts --project=sockshop - After creating the service, Keptn allows to add service-related artifacts like the performance test:
keptn add-resource --project=sockshop --stage=production --service=carts --resource=jmeter/load.jmx --resourceUri=jmeter/load.jmx
Keptn's quality gate is specified by Service Level Objectives (SLOs). In order to pass this quality gate, the service has to meet the SLOs. These SLOs are described in a file called slo.yaml. To learn more about the slo.yaml file, go to Specifications for Site Reliability Engineering with Keptn.
Activate the quality gates for the carts service. Therefore, navigate to the examples/onboarding-carts folder and upload the slo.yaml file using the add-resource command:
keptn add-resource --project=sockshop --stage=production --service=carts --resource=slo-quality-gates.yaml --resourceUri=slo.yaml
For evaluating the SLOs, metrics from a monitoring tool are required. Currently, this tutorial supports Prometheus as a monitoring tool, which is set up in the following steps:
- Install the Keptn Prometheus-service in your Kubernetes cluster.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keptn-contrib/prometheus-service/release-0.3.5/deploy/service.yaml - Install the Prometheus SLI provider in your cluster.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keptn-contrib/prometheus-sli-service/release-0.2.2/deploy/service.yaml - Configure Prometheus as monitoring solution.
keptn configure monitoring prometheus --project=sockshop --service=carts - Configure custom SLIs for the Prometheus SLI provider as specified in
sli-config-argo-prometheus.yaml:keptn add-resource --project=sockshop --stage=production --service=carts --resource=sli-config-argo-prometheus.yaml --resourceUri=prometheus/sli.yaml
This tutorial provides deployment resources (in the form of a Helm chart), which contains the carts and carts-db service. The carts service is of type rollout, which allows a blue/green deployment.
- Argo CD requires a Git repo where this Helm chart is stored and, here, Keptn's config-repo is re-used. Execute the following command and replace
GIT_REMOTE_URLwith the URL as you used before when creating the Keptn project:git clone GIT_REMOTE_URL cd sockshop git checkout production - Copy the
argofolder provided in the examples repo underonboarding-carts/into
the config repo in the foldercarts. - Add, commit, and push the changes:
git add . git commit -m "Add deployment resources" git push
Next, we set up an Argo app. Therefore, this tutorial assumes that you have completed the Argo CD installation and Argo Rollouts installation.
- Create an Argo app using the
argocdCLI. Therefore, the app name has to follow the formatServiceName-StageNameand the namespace has to follow the formatProjectName-StageName:argocd app create --name carts-production --repo GIT_REMOTE_URL --dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc --dest-namespace sockshop-production --path carts/argo/carts --revision production --sync-policy none - Create a namespace in which the app is deployed:
kubectl create namespace sockshop-production
In order to inform Keptn when Argo CD does the deployment,
an Argo Resource Hook is configured. This hook is triggered when Argo CD applies the manifests. This hook executes a script which sends a
sh.keptn.events.deployment-finished event to the Keptn API.
Therefore, this hook needs to access the Keptn API and, hence, requires the Keptn endpoint as well as the api-token.
Please create a secret with the Keptn endpoint and api-token:
KEPTN_API_URL=<KEPTN_API_URL>
KEPTN_API_TOKEN=<KEPTN_API_TOKEN>
kubectl -n sockshop-production create secret generic argo --from-literal="KEPTN_API_URL=$KEPTN_API_URL" --from-literal="KEPTN_API_TOKEN=$KEPTN_API_TOKEN"
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
generateName: app-keptn-notification-
annotations:
argocd.argoproj.io/hook: Sync
argocd.argoproj.io/hook-delete-policy: HookSucceeded
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: keptn-notification
image: agrimmer/alpine-curl-uuid-kubectl:latest
command: ["/bin/sh","-c"]
args: ['while [[ $(kubectl get rollout {{ .Values.keptn.service }}-{{ .Values.keptn.stage }} -n {{ .Values.keptn.project }}-{{ .Values.keptn.stage }} -o "jsonpath={..status.conditions[?(@.type==\"Progressing\")].reason}") == "ReplicaSetUpdated" ]]; do echo "waiting for rollout" && sleep 1; done; UUID=$(uuidgen); UUID=$(uuidgen); now=$(TZ=UTC date "+%FT%T.00Z"); curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/cloudevents+json" -H "x-token: ${KEPTN_API_TOKEN}" --insecure -d "{\"contenttype\": \"application/json\", \"data\": { \"project\": \"{{ .Values.keptn.project }}\", \"service\": \"{{ .Values.keptn.service }}\", \"stage\": \"{{ .Values.keptn.stage }}\", \"deploymentURILocal\": \"http://{{ .Values.keptn.service }}-canary.{{ .Values.keptn.project }}-{{ .Values.keptn.stage }}\", \"deploymentstrategy\": \"blue_green_service\", \"teststrategy\": \"performance\"}, \"id\": \"${UUID}\", \"source\": \"argo\", \"specversion\": \"0.2\", \"time\": \"${now}\", \"type\": \"sh.keptn.events.deployment-finished\", \"shkeptncontext\": \"${UUID}\"}" ${KEPTN_API_URL}/v1/event']
env:
- name: KEPTN_API_URL
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: argo
key: KEPTN_API_URL
- name: KEPTN_API_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: argo
key: KEPTN_API_TOKEN
restartPolicy: Never
backoffLimit: 2
- Sync the Argo app using the ArgoCD UI or the
argocdCLI:argocd app sync carts-production - Check whether the hook triggered Keptn. Therefore, go to Keptn's Bridge and check whether there is a
sh.keptn.events.deployment-finishedevent. - Follow the events in the Keptn's Bridge and compare it to the screenshot below.
- The new version (i.e. the
canary) as well as the released version (i.e. theprimary) of thecartsservice are exposed via a LoadBalancer. In order to access the website of thecartsservice, query the external IPs of the LoadBalancer:kubectl get services -n sockshop-productionNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE carts-canary LoadBalancer 10.3.10.175 35.x.x.x 80:32475/TCP 47h carts-db ClusterIP 10.3.1.153 <none> 27017/TCP 47h carts-primary LoadBalancer 10.3.14.82 35.x.x.x 80:32597/TCP 47h - Navigate to
http://EXTERNAL-IPfor viewing both versions of thecartsservice in yourproductionenvironment.
Expected Result: This version has passed the quality gate. Hence, you should see that both services serve the same content.
You will see these events in the Keptn's Bridge:
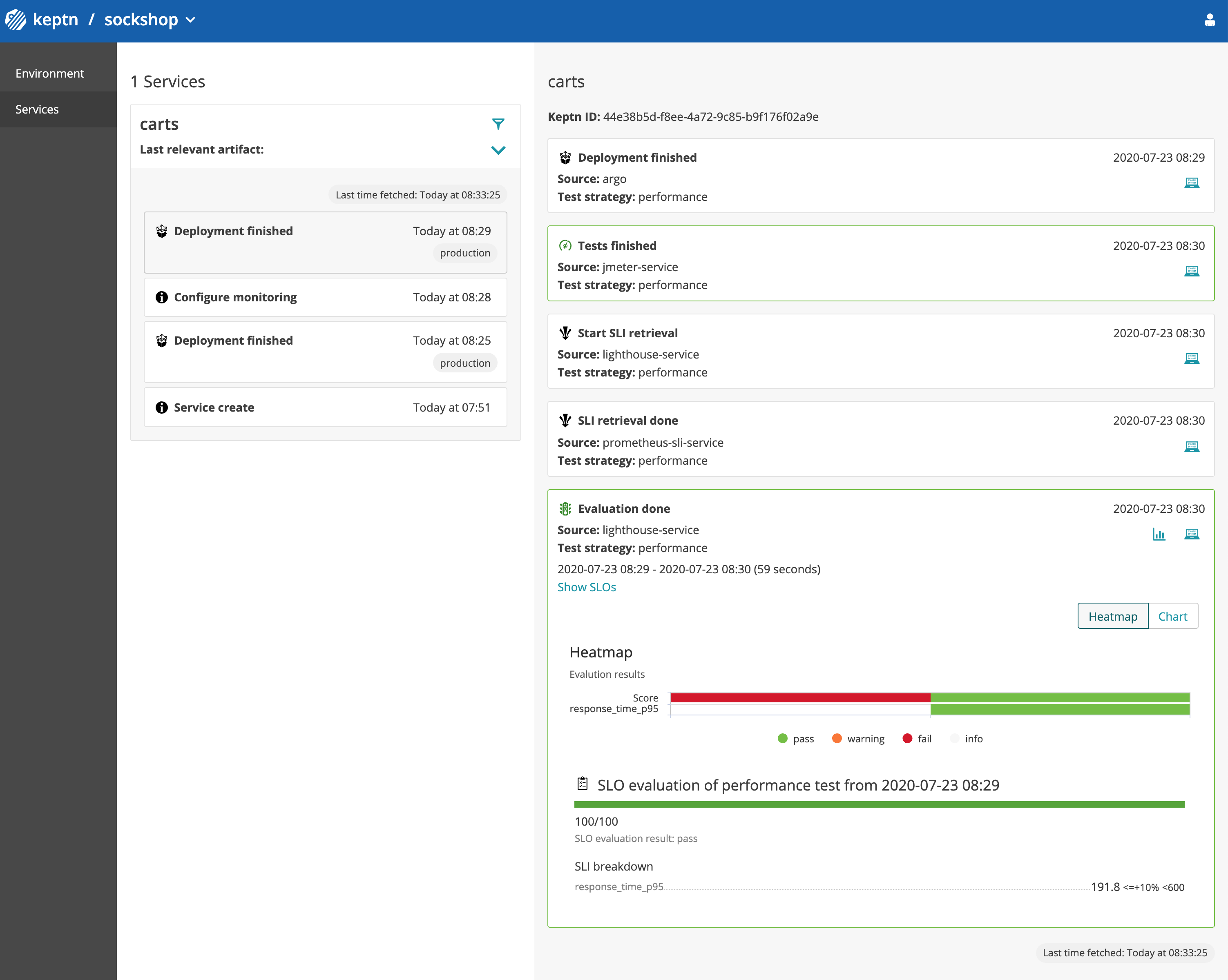
Next, we will deploy a slow version of the carts service, which contains an artificial slowdown of 2 second in each request. This version must not pass the quality gate and, hence, should not be promoted to serve real-user traffic.
- In your Git repository containing the Argo resources, go to the folder
carts/argo/cartsand open thevalues.yamlfile. - Edit the
tagfrom0.11.1to0.11.2. - Add, commit, and push these changes:
git add . git commit -m "Use slow version" git push - Sync the Argo app using the ArgoCD UI or the
argocdCLI:argocd app sync carts-production - Follow the events in the Keptn's Bridge and compare it to the screenshot below. Please note that the performance tests will take approx. 20 minutes.
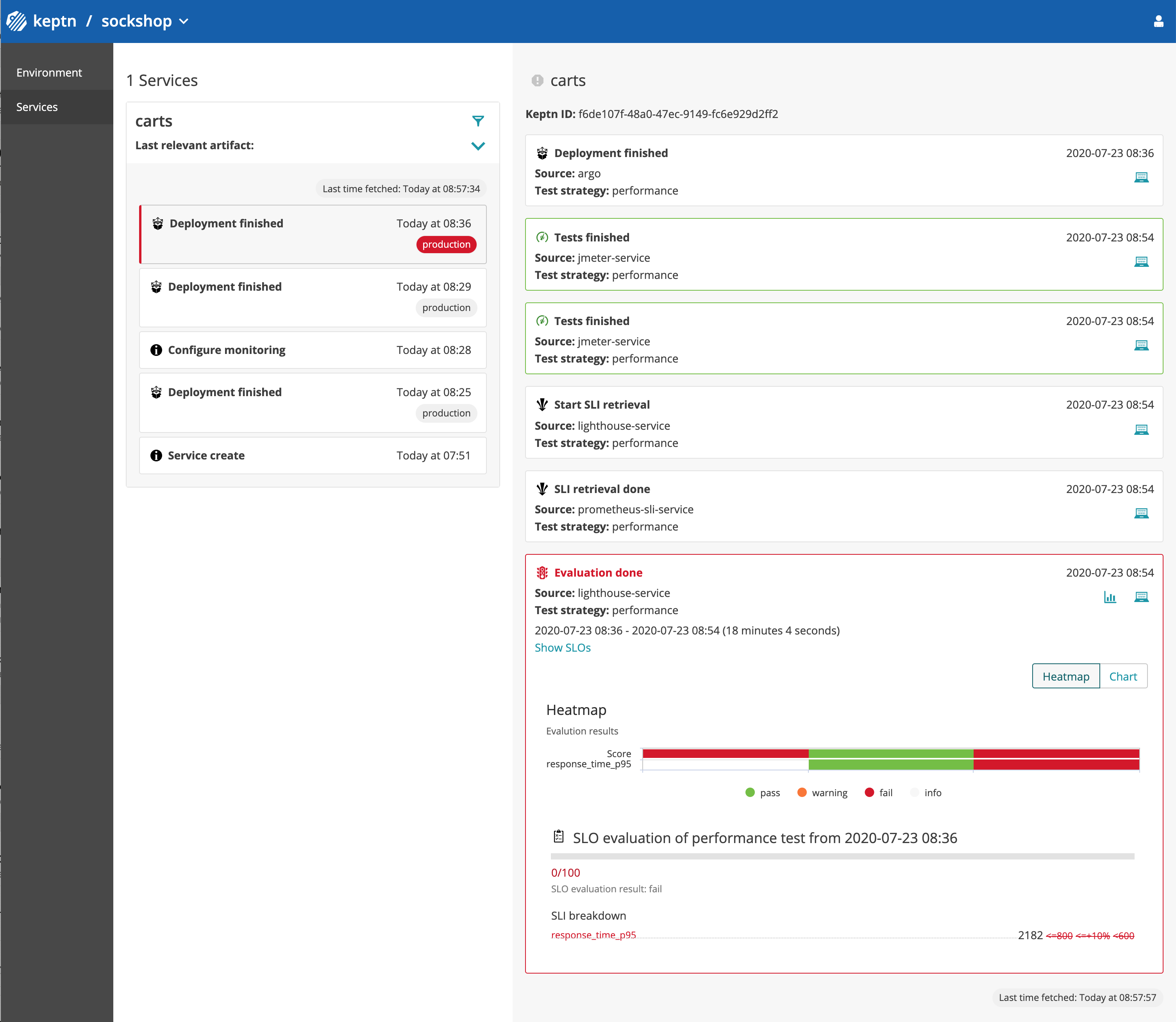
- Navigate to
http://EXTERNAL-IPfor viewing both versions of thecartsservice in yourproductionenvironment.

Expected Result: This version 0.11.2 should not pass the quality gate. The primary version should still show the last version 0.11.1.
Finally, we will deploy a version which does not contain the slowdown anymore.
This version should now again pass the quality gate and, hence, should be promoted to serve real-user traffic.
- In your Git repository containing the Argo resources, go to the folder
carts/argo/cartsand open thevalues.yamlfile. - Edit the
tagfrom0.11.2to0.11.3. - Add, commit, and push these changes:
git add . git commit -m "Use fast version" git push - Sync the Argo app using the ArgoCD UI or the
argocdCLI:argocd app sync carts-production - Follow the events in the Keptn's Bridge and compare it to the screenshot below.
- Navigate to
http://EXTERNAL-IPfor viewing both versions of thecartsservice in yourproductionenvironment.
Expected Result: This version 0.11.3 should pass the quality gate. The primary version should show version 0.11.3.

Your Bridge should show an event flow similar to the one in this screenshot:
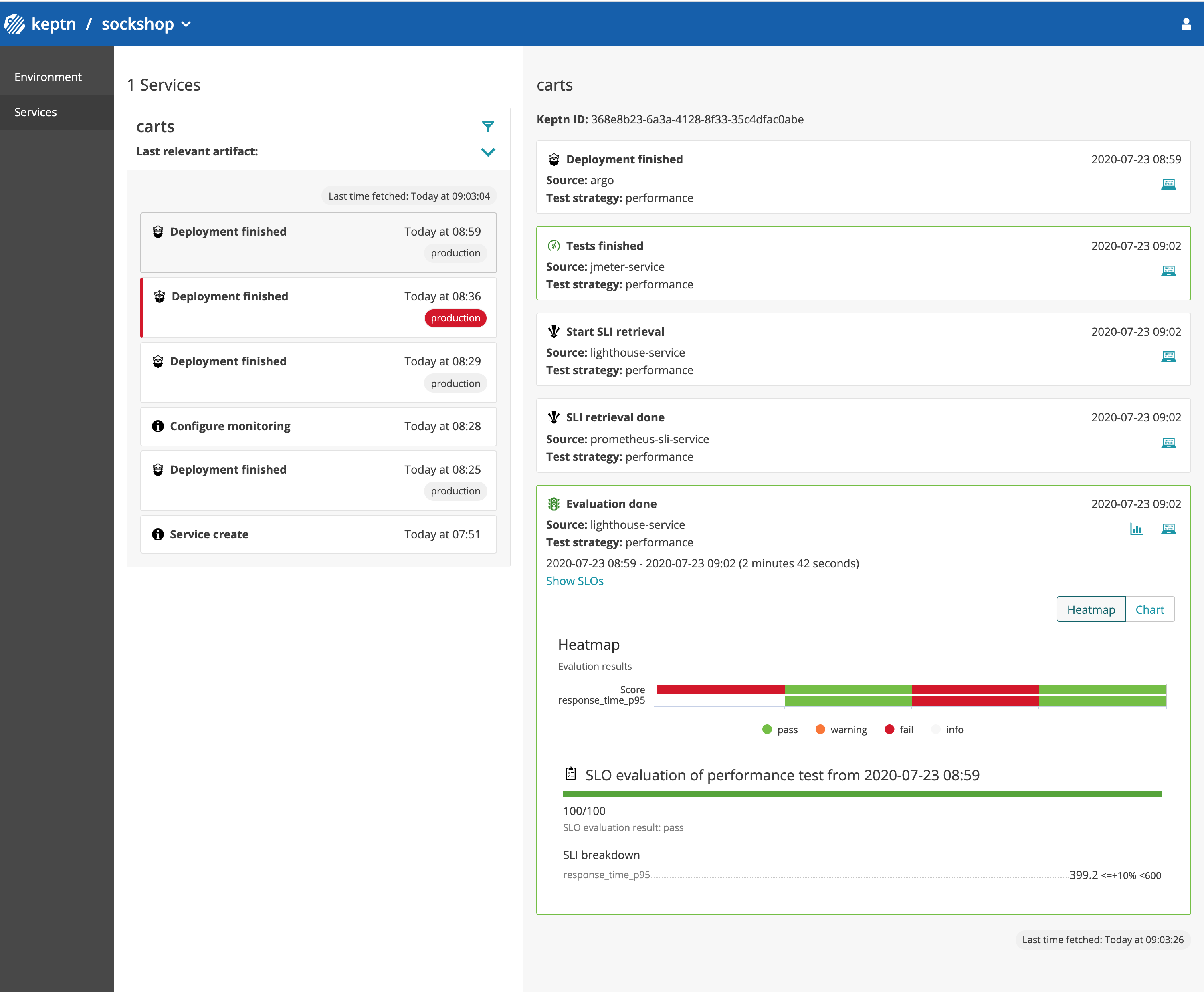
Congratulations!
You have successfully finished the tutorial on using ArgoCD/Rollouts for deployment and Keptn for testing, evaluation and promoting your microservices.